Yeast is sustainable for the environment by cutting pollution and waste
Yeast producers have demonstrated a sustained commitment to preserving the environment and sustaining natural habitats. Yeast manufacturing was one of the very first biotechnology industries which have embraced from the beginning cutting-edge technologies to develop new methods of water, energy, and waste management.
Pollution and waste are two major challenges to our society, and they can come in many forms. Recycling is a key element of the circular economy that contributes to the protection of natural resources and the reduction of this pollution. Recycling reduces our need for water, natural resources, and CO2 emissions (-700 million tons of CO2 emissions/per year)(1). Recycling can also help to change unused resources into new treasures that would otherwise become waste and add to the problem.
Water is key in the yeast manufacturing process, but water is also considered to be a precious resource. By introducing major water-saving initiatives and by recycling water, consumption has been reduced by more than 20% in the past 20 years in much of the yeast industry.(2)
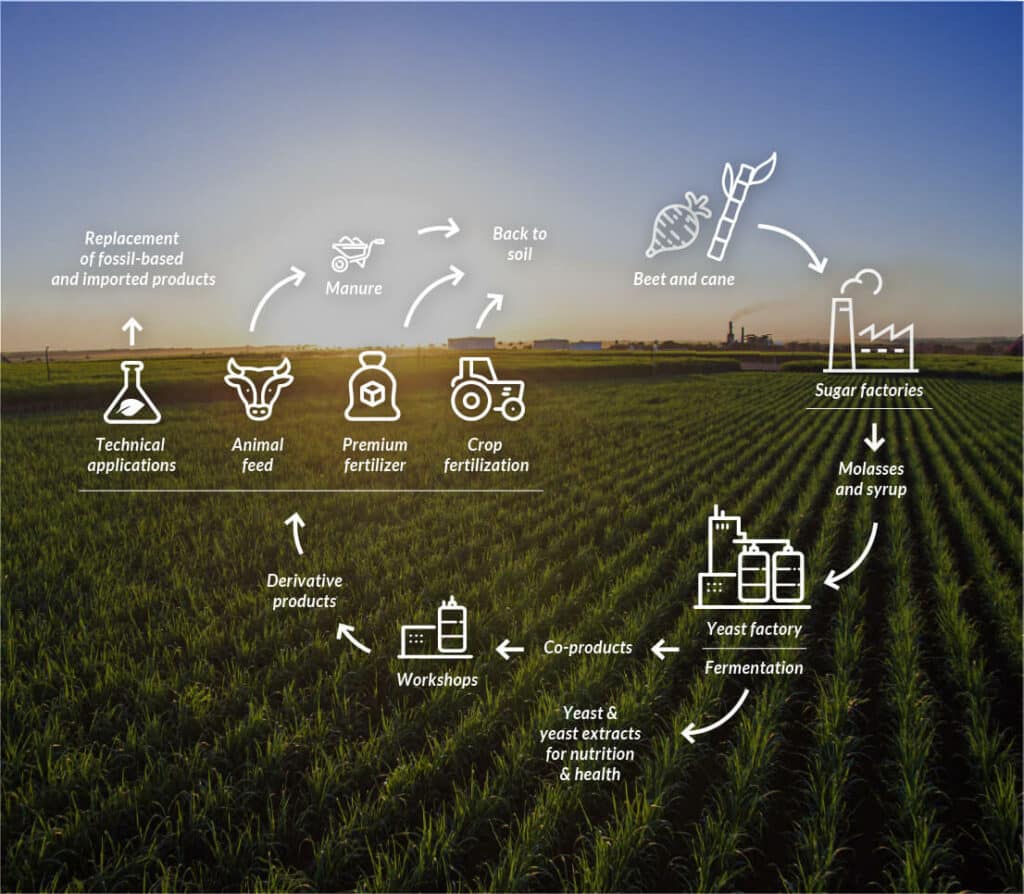
In much of the yeast industry energy used to drive fermentation is carefully managed. Waste is processed using anaerobic digesters and yeast producers are increasingly relying on renewable energy. Furthermore, yeast factories are one of the major consumers of molasses. Molasses is a by-product of the sugar industry and without being used would simply be discarded and go to waste. However, yeast producers have been able to recycle this treasure and use it as the preferred feedstock for yeast production!
For European yeast manufacturers, nearly 90% of the molasses is sourced in Europe, which helps to maintain a regional supply chain and again contributes to keeping the carbon footprint to a minimum(3). After yeast is made the waste by-products from fermentation can be transformed into natural fertilizers used in agriculture.
So, yeast not only helps reuse the waste products of other industries but its by-products can be used to support and contribute to the success of other industries safely and sustainably!
Yeast can help sustainably nourish the world
Faced with a rising global population and the increasing scarcity of animal protein, nourishing 9 billion persons in 2050 sustainably and healthily is one of the major societal concerns of this century.
Bread is a major source of plant proteins and is a low-cost staple food. Bread has historically been a means of feeding the world population and will continue to be a solution in the future to meet the global population’s food needs. As an essential ingredient in bread, baker’s yeast is thus at the heart of these societal challenges!
Learn more about bread and yeast!
Furthermore, yeast proteins and things like nutritional yeast can constitute an alternative to animal proteins to help the world’s population be more sustainable and move away from these highly resource-intensive means of protein. The environmental benefits of yeast proteins to combat climate change and preserve biodiversity compared to animal-origin proteins are significant and will continue to play a big part in the evolution of society towards sustainability.
Discover more about yeast extracts!
Lastly, modern diets have become rich in salt, which can lead to many health risks(4). Yeast and yeast extract as ingredients have the potential to play a major role in salt reduction while keeping food flavorful. By using yeast and yeast extract instead of salt to naturally bring out the taste of food, it may be possible to reduce salt use in food preparation by up to 30%(5). By reducing salt intake, yeast can help to contribute to reducing the risks of cardiovascular disease and hypertension. This means a more sustainable future for both the planet’s health and human health!
Explore the health benefits of nutritional yeast
Yeast can start a sustainable revolution!
The World Health Organization has developed the “One Health” approach, to view human health, animal health, and environmental health as interconnected(6). To protect the health of every living being and our ecosystems, sectors must work together to resolve the challenges of food sufficiency and food security, management of zoonoses (diseases that can transmit from animals to humans), and combat the emergence of antibiotic resistance.
Yeast is the answer to a more sustainable future and achieving “One Health.” First, yeast can use the waste of other industries turning it into a treasure. Then organic matter from the production of yeast and yeast ingredients can, among other things, be reused as fertilizer, as a source of protein essential to animal nutrition, and, after processing, as an alternative to other less virtuous products in the industry. Furthermore, yeast can support sustainability in the food supply and help our growing population by being an essential ingredient in bread and an alternative protein while at the same time reducing the use of salt so that we can promote better health for all!
The different applications of yeast are numerous, and we are discovering new potential applications every day! The power of yeast can start a revolution to support a more sustainable future for all!